Why is Blockchain Important? 2024
Blockchain technology, often hailed as the cornerstone of the digital revolution, has gained unprecedented momentum in recent years. Its decentralized, secure, and transparent nature has made it a game-changer across various industries.
In this article, we will delve into the profound impact of blockchain, exploring why it’s reshaping businesses, ensuring trust, and challenging traditional practices – and ultimately answering the question: why is blockchain important?
Table of content
Highlights of the Article
- Blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates the need for a central authority, ensuring trust among participants.
- Cryptographic techniques, encryption, and immutability protect data from tampering or fraud.
- Self-executing smart contracts streamline processes, reduce costs, and eliminate intermediaries.
- Blockchain enables end-to-end traceability, counterfeit prevention, and streamlined processes in supply chains.
- Blockchain provides banking services to the unbanked and facilitates cross-border transactions.
- Tokenization represents real-world assets digitally, enabling fractional ownership and increased liquidity.
- Despite initial energy concerns, blockchain’s potential role in sustainability is being addressed through innovations.
- Scalability, regulatory concerns, education, and environmental considerations need attention.
- Layer 2 solutions, integration with emerging technologies, government and enterprise adoption, and disruptions in traditional industries are anticipated trends.
- Blockchain’s trustworthiness relies on decentralization, transparency, and immutable record-keeping, and it has far-reaching implications for various industries.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
Here are some of the key advantages:
✔️ Decentralization and Increased Security: Blockchain operates on a decentralized computer network, making it highly secure. Since there’s no central control point, it’s resistant to hacking, fraud, and unauthorized alterations.
✔️ Transparency and Immutability: All transactions recorded on a blockchain are transparent and immutable. Once a transaction is added, it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures a high level of trust among participants.
✔️ Reduced Intermediaries: Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries like banks, lawyers, and notaries. This reduces costs, speeds up processes, and eliminates the potential for errors or fraud.
✔️ Smart Contracts for Automation: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They automatically execute actions when predefined conditions are met. This reduces administrative tasks, enhances efficiency, and ensures accurate contract execution.
✔️ Improved Traceability and Provenance: In supply chain management, blockchain enables end-to-end traceability of products. This ensures authenticity and quality assurance, crucial in industries like food safety and luxury goods.
✔️ Financial Inclusion and Access: Blockchain allows individuals without access to traditional financial systems to participate in the global economy. It enables secure storage and money transfer, particularly in regions with limited banking infrastructure.
✔️ Fraud Prevention and Security in Finance: Blockchain’s cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms make it highly resistant to fraud. This is particularly valuable in financial transactions, where security is paramount.
✔️ Tokenization for Increased Liquidity: Tokenization allows real-world assets to be represented digitally. This enables fractional ownership, making high-value assets accessible to a broader audience and increasing liquidity.
✔️ Global Accessibility and Cross-Border Transactions: Blockchain facilitates cross-border transactions with reduced fees and faster processing times. This is particularly important for remittances and international trade.
✔️ Enhanced Privacy and Data Control: Blockchain gives individuals more control over their data. They can choose what information to share and with whom, potentially reducing the risk of data breaches.
✔️ Improved Efficiency in Record-Keeping: In sectors like healthcare, blockchain ensures the integrity and privacy of patient records. It streamlines data sharing among authorized parties, reducing administrative overhead.
✔️ Environmental Impact and Sustainability: While energy consumption has been a concern, advancements in consensus mechanisms and sustainable blockchain practices address these issues. Blockchain also has potential applications in tracking and verifying sustainable practices.
Overall, the benefits of blockchain technology are vast and diverse, and its potential to disrupt traditional industries and improve efficiency is significant.
FAQ
⭐ What is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology employs a distributed ledger to record transactions across multiple nodes. Transactions are recorded in chronological order and stored in blocks that are linked together.
⭐ How does blockchain work?
Blockchain utilizes a network of computers (nodes) to validate and record transactions. Once verified, transactions are grouped into blocks and added to a chain in a linear, chronological order. This ensures that the ledger is secure, tamper-proof, and transparent.
⭐ What is decentralization in blockchain?
Decentralization means that the blockchain network is not controlled by a single entity or authority but maintained by a distributed network of nodes. This reduces the risk of fraud, manipulation, or system failure.
⭐ What are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are contracts with the terms written into code. They execute actions when certain conditions are met, eliminating intermediaries.
⭐ Can blockchain be hacked?
Blockchain is highly secure due to its cryptographic and decentralized nature. However, no system is entirely invulnerable. A 51% attack could occur if a single entity controls most of a blockchain’s computing power.
⭐ How does blockchain improve transparency in sports?
Blockchain in sports industry ensures transparent record-keeping and secure data sharing, reducing fraud and manipulation risks.
Decentralization and Trust
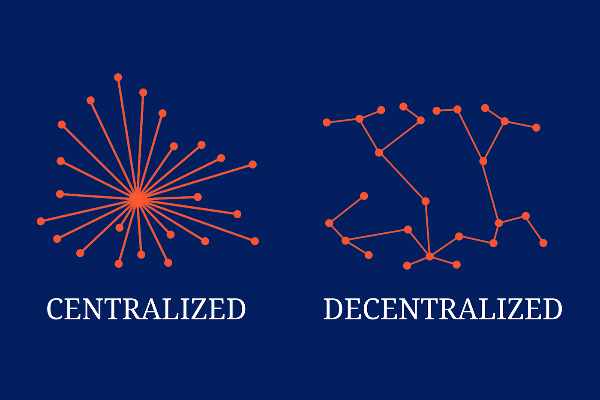
Centralized vs. Decentralized Systems
Centralized systems, long the bedrock of many industries, rely on a single authority or intermediary to validate and record transactions. This poses inherent risks, including data manipulation, censorship, and single points of failure.
Conversely, blockchain leverages a decentralized network of nodes, each holding a copy of the ledger. Transactions are verified through a consensus mechanism, eliminating the need for a central authority and vastly improving trust.
Trust Issues in Centralized Systems
Centralization inherently leads to trust concerns. Instances of data breaches, fraudulent activities, and lack of transparency have eroded public trust in centralized systems. Institutions like banks, traditionally holding our financial records, are now facing increasing scrutiny.
Blockchain addresses these issues through its distributed ledger, where every transaction is recorded in a transparent and immutable manner. This ensures that once information is added, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a level of trust previously unattainable.
How does Blockchain Ensure Trust?
Below, you can find the fundamental principles underpinning blockchain’s trust – decentralization, transparency, and immutable record-keeping.
Decentralization
Trust is vested in a single authority or intermediary in traditional centralized systems. This, however, introduces a vulnerability: if this central authority is compromised, trust is eroded. Blockchain addresses this critical issue through decentralization.
Instead of relying on a single entity, blockchain employs a distributed network of nodes, each maintaining a copy of the ledger.
Transactions are verified through consensus mechanisms, meaning that most nodes must agree on the validity of a transaction. This eliminates the need for a central authority, making the system highly resistant to manipulation or corruption.
Transparency
Blockchain’s transparency is a linchpin in ensuring trust. Every transaction on a blockchain is recorded in a public ledger, accessible to all participants in the network.
This means that every party involved can scrutinize the entire transactional history. The transparency of blockchain provides a level of accountability unparalleled in centralized systems.
It acts as a powerful deterrent against fraudulent activities, as any attempt to alter the ledger would require a consensus from the majority of nodes in the network. This open and transparent ledger fosters a culture of trust among participants, instilling confidence in the system’s integrity.
Immutable Record-Keeping
Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes a permanent part of the ledger. This immutability is a cornerstone of blockchain’s trustworthiness.
It is achieved through cryptographic hash functions, which generate a unique identifier for each block. These identifiers are linked to the previous block, creating an unbreakable chain.
Attempting to alter a transaction after it’s been recorded would require immense computational power and consensus from most nodes, making fraudulent activities virtually impossible.
This feature ensures that once information is added, it cannot be tampered with, providing a level of trust crucial in critical applications like financial transactions and sensitive record-keeping.
In summary, blockchain’s trustworthiness is rooted in its decentralization, transparency, and immutable record-keeping. These principles work in concert to create a system where trust is not reliant on a central authority but is instead distributed among the network’s participants.
Smart Contracts and Automation
Blockchain’s innovation doesn’t end with secure transactions; it extends to smart contracts. These self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions revolutionize agreements across various industries.
Definition and Function of Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are pieces of code stored on a blockchain that automatically execute actions when predetermined conditions are met. They eliminate the need for intermediaries, ensuring transparency and efficiency in contract execution.
Advantages of Smart Contracts: Firstly, they enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Tasks that typically require time and resources for verification and enforcement are automated. Secondly, they eliminate intermediaries like lawyers and notaries, lowering transaction costs.
Finally, they ensure transparency and accuracy, as all terms are written in code and recorded on an immutable ledger.
Use Cases: Real estate transactions are being transformed by smart contracts. They enable seamless property transfers, reducing the risk of fraud. In the legal sector, contracts automatically execute once conditions are met, streamlining legal processes.
Additionally, smart contracts automate tasks like quality checks and payments in the supply chain, significantly improving efficiency.
Tokenization and Asset Management
Tokenization is a groundbreaking application of blockchain technology that represents real-world assets digitally. It’s poised to disrupt traditional financial systems, offering increased accessibility and liquidity.
Definition: Tokenization involves representing real assets, such as real estate, art, or intellectual property, as digital tokens on a blockchain. Each token is backed by a fraction of the physical asset, enabling fractional ownership.
Benefits: Firstly, it allows for fractional ownership, making high-value assets accessible to a broader audience. Secondly, it enhances liquidity, as tokens can be traded on secondary markets. Finally, it opens up opportunities for global investment, democratizing access to premium assets.
Use Cases: Real estate, traditionally an illiquid investment, is revolutionized by tokenization. Investors can now own fractions of properties, diversifying their portfolios. Art, too, is becoming more accessible, with individuals able to own shares in valuable pieces.
Even intellectual property rights can be represented as tokens, allowing creators to monetize their work in new ways.
Environmental and Sustainability Impacts
Blockchain technology, while revolutionary, has faced criticism for its energy consumption. However, it also presents opportunities for sustainability through innovation and strategic implementation.
Energy Consumption Debate:
Blockchain mining, particularly in Proof of Work (PoW) systems, has been criticized for its energy-intensive nature. This has raised concerns about its environmental impact, especially in an era focused on reducing carbon footprints.
Innovations in Energy-Efficient Blockchain:
The blockchain community actively works on solutions to reduce energy consumption. Transitioning from PoW to Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms can significantly decrease energy usage.
Layer 2 solutions like Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Ethereum 2.0 are designed to enhance scalability and reduce energy expenditure.
Blockchain’s Potential Role in Sustainability:
Blockchain’s transparency and traceability can be leveraged to monitor and validate sustainable practices. For example, it can track the origin and journey of products, ensuring they meet environmental standards. Additionally, blockchain-based systems can facilitate carbon credit trading, incentivizing green initiatives.
Use Cases:
Blockchain is being applied in the renewable energy sector, enabling transparent tracking of energy production and distribution. It ensures that consumers use clean energy and supports the growth of renewable sources.
Blockchain Challenges and Potential Limitations
While blockchain holds immense promise, it’s has its challenges. Addressing these issues is crucial for the technology’s widespread adoption and long-term success.
- Scalability Issues: As blockchain networks grow, scalability becomes a critical concern. Current infrastructure struggles to handle high transaction volumes, leading to delays and increased fees. Solutions like sharding and Layer 2 protocols are being developed to address this.
- Regulatory Concerns: Governments worldwide are grappling with how to regulate blockchain and cryptocurrencies. Striking a balance between innovation and compliance is essential to ensure the technology’s legitimacy.
- Education and Adoption Barriers: Blockchain is a complex technology with limited widespread understanding. Educating individuals and businesses about its benefits and applications is vital for mainstream adoption.
- Addressing Environmental Concerns: The environmental impact of blockchain, particularly energy consumption, is a significant concern. Transitioning to more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and promoting sustainable blockchain practices is crucial.
Future Trends and Developments
Blockchain technology is poised for continued evolution and integration with emerging technologies, promising even greater transformation across various industries.
Layer 2 Solutions and Scalability Improvements:
The development of Layer 2 solutions, such as the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and state channels for Ethereum, aims to alleviate scalability challenges. These solutions allow for faster and more cost-effective transactions while maintaining the security of the underlying blockchain.
Integration with Emerging Technologies:
Blockchain is converging with other transformative technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). This convergence is creating powerful synergies, enabling new applications and use cases.
For example, blockchain can enhance the security and transparency of IoT devices, while AI can optimize blockchain processes.
Government and Enterprise Adoption:
Governments and large enterprises recognize blockchain’s potential to drive efficiency, transparency, and innovation. We expect increased adoption in supply chain management, identity verification, and regulatory compliance.
Potential Disruptions in Traditional Industries:
Industries traditionally relying on centralized systems and intermediaries, such as finance, healthcare, and legal, are poised for significant disruption. Blockchain’s ability to streamline processes, enhance security, and reduce costs makes it a powerful force for change.
Summary
To sum up, blockchain technology is one of the most transformative innovations of our time. Its decentralization, security, and transparency have the potential to revolutionize industries and reshape how we conduct business.
Blockchain drives efficiency and inclusivity by addressing trust issues, enhancing security, and automating processes through smart contracts.
The applications of blockchain are vast and varied, from ensuring the authenticity of products in the supply chain to providing financial services to the unbanked. Despite challenges, including scalability and regulatory concerns, the future of blockchain looks promising.
We expect to see even greater disruptions in traditional industries as they continue integrating with emerging technologies and gaining traction in government and enterprise sectors.